What is 3D printing?
- An additive manufacturing process for construction of 3D object from CAD file
- Different techniques of 3D printing, including
- Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) or Fused Deposition modeling (FDM) (https://3dprinterpower.com/fff-vs-fdm/)
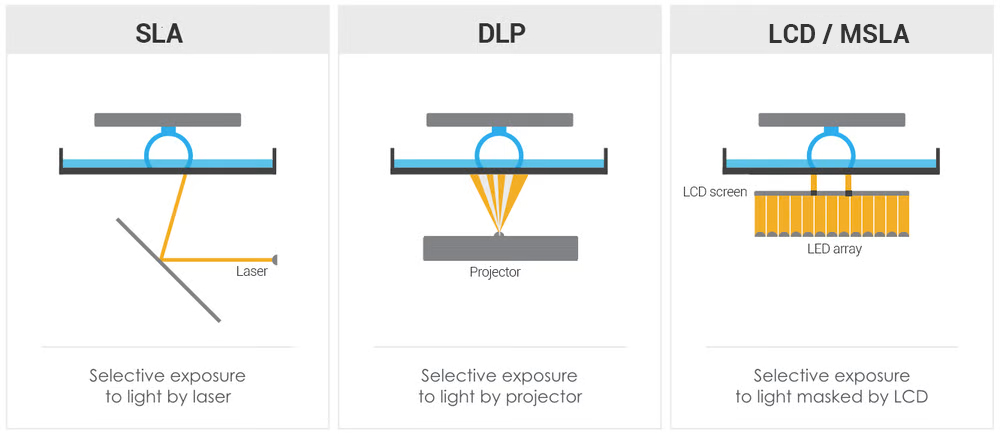
- Stereolithography (SLA), DLP or LCD (https://all3dp.com/2/dlp-3d-printer-digital-light-processing-explained/) - resin-based approach
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) (https://youtu.be/sRC8W77MlrY?si=oVZ7CkE36utrWrUR) - powder-based approach
- Comparison between FDM, DLP, SLA
- More printer types
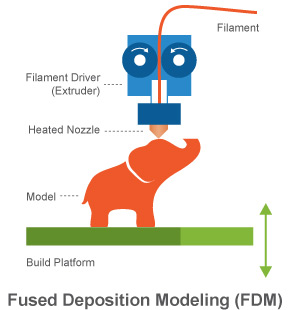
How does FFF/FDM work?
(source: https://all3dp.com/2/fused-filament-fabrication-fff-3d-printing-simply-explained/)
(source: How Does The FDM 3D Printing Technology Work? | Manufactur3D)
Important concepts:
- Filament is brought in by "cold end" and heat up to molten form at "hot end" and squeeze out through nozzle
- Squeezed out molten material (extruded material) get deposited onto the 3D object under construction, layer by layer
(source: Fused Filament Fabrication – Simply Explained | All3DP)
Benefits of FFF
- Large selection of materials, including many common thermoplastics, wood and metal-infused thermoplastics, and even food (such as chocolate).
- Least expensive printer technology.
- Least expensive materials.
- Easy to switch materials.
- Possible to print using multiple different materials.
- Printers and materials offered by many manufacturers.
- Relatively easy to build your own printer.
- Fast printing.
Major disadvantages of FFF
- The detail of finished prints is limited by the size of the nozzle. Other technologies offer higher detail.
- The strength of finished parts is limited because each layer is joined to the layer below it.
- Need to waste some support material due to gravity
(source: Introduction to Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) - University of Maryland) - Have layer pattern on the side
source: Fused Filament Fabrication – Simply Explained | All3DP
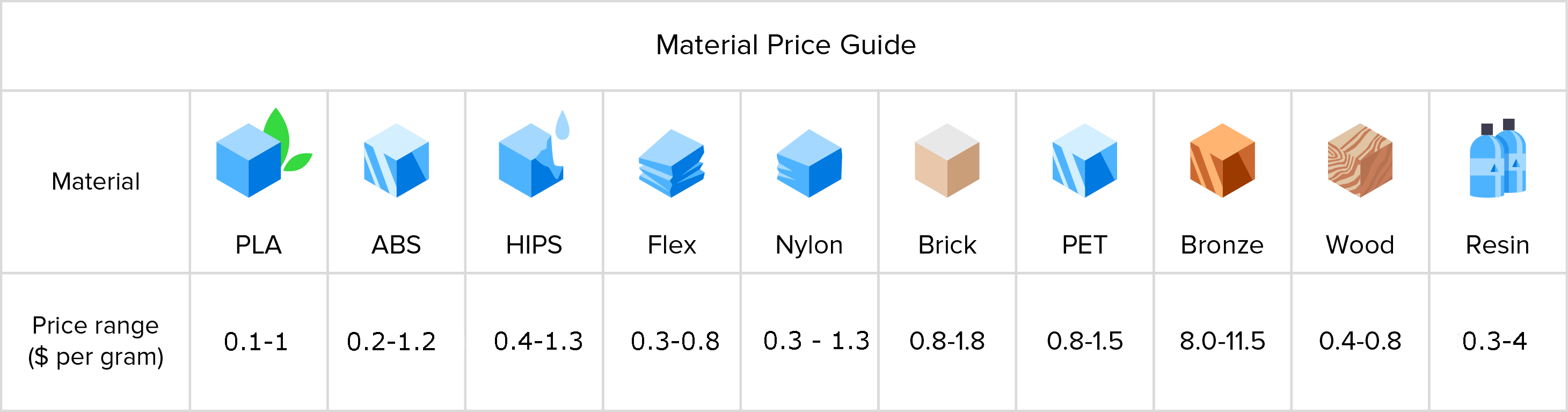
Material
Build material
PLA (Most commonly use)
- melting point: 180C to 220C
- soften at 60C (glass transition temperature)
| Material | Properties |
|---|---|
| PLA (polylactic acid) | Excellent surface quality and detail. Mechanical and heat properties not suitable for some applications |
| ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) | Strong, ductile material with wear resistance and heat tolerance |
| Nylon (polyamide) | Strong yet flexible, with good chemical, impact, and abrasion resistance |
| PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified) | Good toughness and wear resistance, with chemical resistance against many industrial fluids. |
| CPE (copolyester) | Durable and flexible with a glossy finish and good impact and heat resistance |
| PC (polycarbonate) | Strong and tough material with heat resistance up to 110 °C |
| TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) | Flexible material with rubber-like properties. Provides high impact and wear resistance |
| PP (polypropylene) | Durable, tough, and fatigue resistant. Retains shape after torsion, bending, or flexing |
| PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) | Water-soluble material used to create supports for overhangs and cavities |
source: What is FFF 3D printing? - UltiMaker
source: How much should I charge to make prints? Help Center
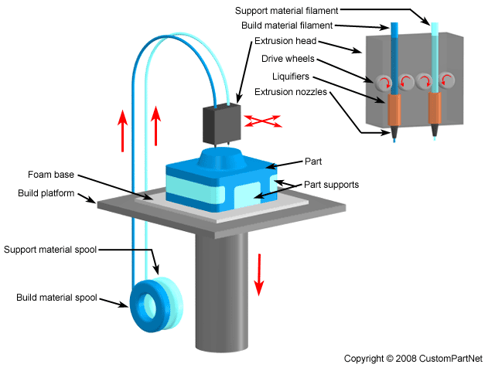
Support material
Using normal build material for support:
The following is some introduction of Bambu support filaments:
Types of support filaments | Support W, i.e. Support for PLA | Support for PLA/PETG | Support G, i.e. Support for PA/PET | |
Types of body filaments that are compatible | PLA, PLA-CF, etc. | PLA, PLA-CF, PETG, PETG-CF, etc. | PLA, PLA-CF, PETG, PETG-CF, etc. | PA, PA-CF/GF, PA6-CF/GF, PAHT-CF/GF, PET-CF/GF, etc. |
Characteristics | 1. Easy to remove; 2. High surface quality; 3. Insensitive to moisture, and not strict with drying and moisture proofing | 1. Water-soluble, and suitable for those models that are not convenient to remove with hands and tools; 2. Easy to remove; 3. High surface quality; 4. Sensitive to moisture, and very strict with drying and moisture proofing. 5. Please refer to this wiki before use: PVA Printing Guide. | 1. Easy to remove; 2. High surface quality; 3. Sensitive to moisture, and very strict with drying and moisture proofing. | |
Recommended settings | 1. In most printing cases, it‘s recommended to print the support interfaces with support filaments, and print the support bases with body filaments, so that a lot printing time can be saved. 2. In some special printing cases, it's able to print both the support interfaces and the support bases, i.e. the whole support structures, with support filaments. However, it may leads to bad printing results when it comes to support structures that are thin and tall and deforming or falling during printing. | |||
*Bambu only have 1 nozzle, the following picture just for showing we can use support material for support part in FDM printing. Bambu is able to switch material on same layer by using AMS.
(source: A Guide to FDM Printale Plastics and 3D Printing Filament | 3devo)
Extra:
3D Printing Materials Explained: Compare FDM, SLA, and SLS
Factor affecting printing quality
Filament quality (e.g. brittle when filament absorbs moisture over time)
What Effect Does Moisture Have on 3D Printer Filament Storage?
(source: What Effect Does Moisture Have on 3D Printer Filament Storage?)
PETG quality difference with different moisture contamination
Flow Rate and Filament Moisture
Mass flow rate is directly correlated with the moisture content of 3D printed filament. Higher moisture content yields the lowest viscosity and the highest mass flow rate.
While high flow rates are generally desirable, an unregulated flow rate leads to over extrusion.
Indications of Possible Moisture Content in Failed 3D Printing Builds
- Filament cracks or makes popping noise as the filament is pushed through the extruded
- Holes in the top of parts
- Extruder tip bubbles with a tiny burst of steam, stringy or drooly
- The filament will not adhere to the print bed
- Repeated builds seem inconsistent or fail no changes in variables
- Extruder motor stops but filament keeps coming out
- Extruder motor starts but filament extrusion is delayed
- Parts become soft, fragile, and break easily
- Extruder jams
How to quickly check if the PLA filament is wet
Nozzle temperature (melting point)
whether printing material is melt properly
heat bed or build plate temperature (glass transition temperature)
whether extruded material can stick onto the build plate
enclosure temperature
whether temperature of the object under printing can be properly controlled so that extruded material can stick to subsequent layers